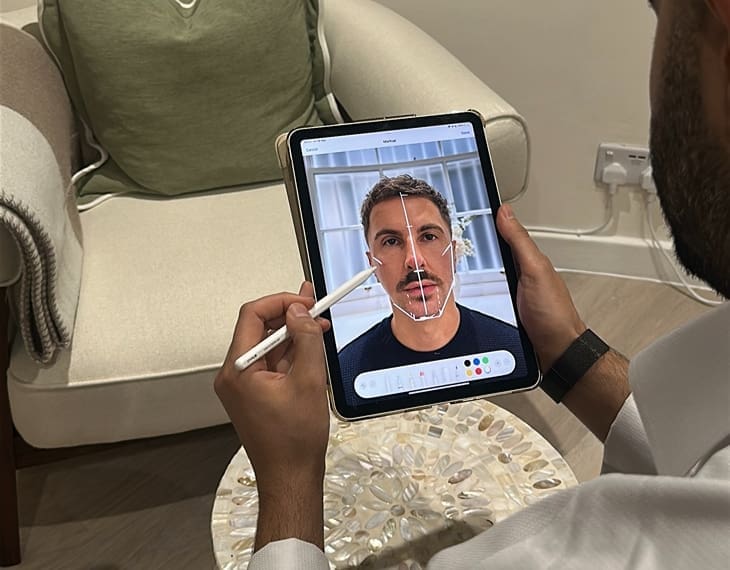
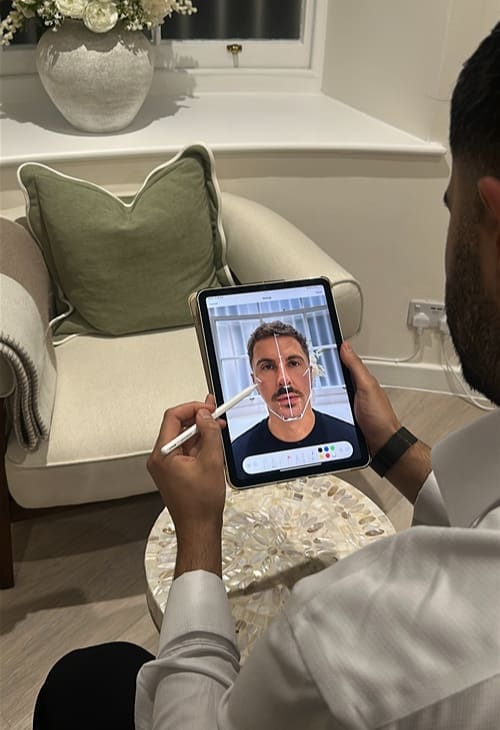
Jaw surgery, also known as orthognathic surgery or mandibular contouring, is a surgical procedure that reshapes or repositions the jawbone to correct alignment, improve facial balance or change the overall facial structure.
Why People Choose Jaw Surgery
Jaw surgery is typically performed for one of two main reasons:
- Functional or medical correction – to address bite problems, misalignment, or skeletal irregularities that affect chewing, breathing, or speech.
- Cosmetic enhancement – to alter the natural jaw shape, reduce jaw width or protrusion, or create a more balanced facial profile.
How Jaw Surgery Works
The procedure is performed under general anaesthesia in a hospital setting by a maxillofacial or plastic surgeon. Depending on the goal, the surgeon may cut and reposition parts of the upper or lower jawbone, sometimes adding or removing bone to achieve the desired structure. Metal plates, screws or wires are often used to stabilise the new bone position during healing.
The operation typically lasts several hours and is followed by an inpatient hospital stay. Recovery involves significant swelling, bruising and dietary restrictions while the bones heal.
Advantages of Jaw Surgery
- Permanent structural change
The results are long-lasting, offering a permanent solution for structural or alignment concerns.
- Comprehensive correction
It can address both functional and aesthetic issues, such as bite misalignment, jaw asymmetry or over/under-projection.
- Major transformation
Surgery can dramatically alter the facial profile, often transforming the appearance of the chin, cheeks and lower face.
Limitations and Considerations
- Highly invasive
Requires general anaesthesia, bone cutting and fixation, which carry significant medical risks.
- Extended recovery
Most patients experience several weeks of swelling and restricted movement, with complete recovery taking up to six months.
- Limited flexibility
Once the jawbone is repositioned, the results are permanent and difficult to adjust.
- Higher risk and cost
The procedure is costly and can lead to complications such as infection, nerve injury or dissatisfaction with appearance.
Jaw surgery is best suited for individuals who need substantial skeletal correction rather than those seeking subtle or cosmetic improvements.